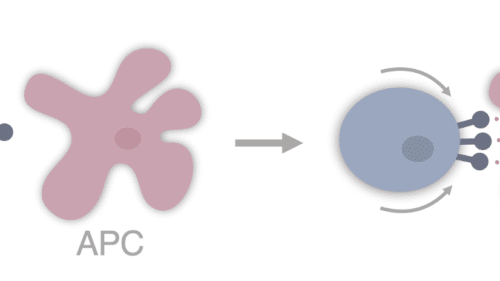
Study of the APC:T-cell interactions
COMMUNICATION
Cell-cell communications play a vital role in activating the body’s immune system. During adaptive immune responses, antigen-presenting cells (APCs) convert foreign antigens into peptides, which are loaded into major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. T cells patrolling the body scan APC and establish intercellular contacts when they recognize a foreign peptide/MHC complex on the APC.
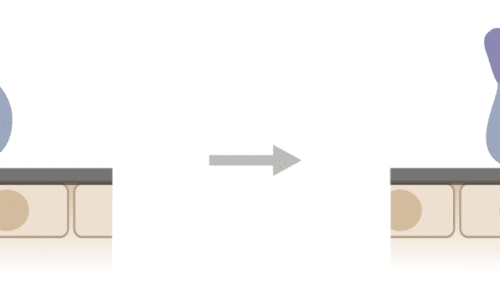
Study of Immune Cell Migration, and transmigration through membranes, in response to chemokines
CELL MIGRATION
ATTACHMENT AND MOVEMENT
The immune system is a dynamic, highly organized, network of cells. Immune cells are capable of motion and migrate to specific organs in a specific manner based on the circumstances. Coming into spatial proximity with other cells they will exchange information and function. These interactions result in diverse immune responses in different situations. When they reach their destined organs, immune cells move further over relatively shorter distances to reach the appropriate destination within the organs. This intra-organ movement is critical and determinative of immune outcomes. The inter- and intra-organ movement of immune cells is guided by a set of secreted molecules called chemokines.
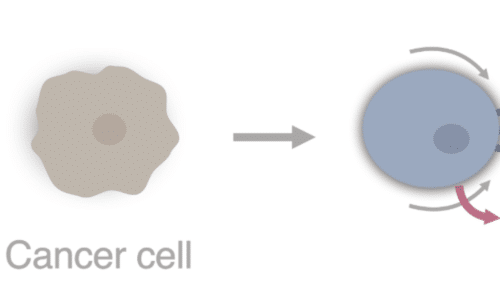
Studying of Cancer cell killing
ACTION
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), natural killer (NK) cells and CAR-T binding to cancer cells carry out their killing function by releasing two types of preformed cytotoxic protein: the granzymes, which seem able to induce apoptosis in any type of target cell, and the pore-forming protein perforin, which punches holes in the target-cell membrane through which the granzymes can enter.
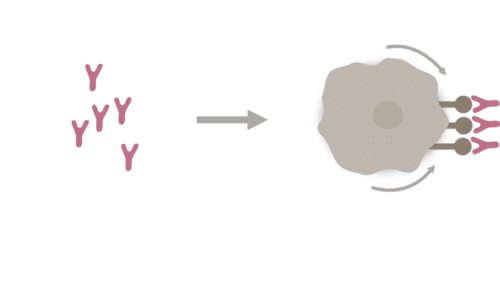
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated-cytotoxicity (ADCC)
ANTIBODY DRUG MODE-OF-ACTION
One of the major mechanisms of action for rituximab is antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), which is mediated by natural killer (NK) cells e.g. Rituximab clusters CD20 on B-cell cancers, recognized by NK-cells activating ADCC. Treatment with rituximab as a single agent has resulted in significant responses in patients with almost every subtype of B-cell lymphoma.
